Cloud computing has revolutionized business transformation, with organizations turning to the cloud to manage their high volumes of structured and unstructured data and critical applications.
Many organizations with workloads in the cloud often experience security incidents. In the last few years, we have witnessed how cybercriminals blackmailed businesses into making payments for regaining access to their systems in denial-of-service attacks (DDoS attacks). Many companies that suffered data breaches compromised the data of their customers. An increase in data security and regulatory compliance regulations has also made cloud security more critical than ever before.
As organizations continue to deploy their IT assets to the cloud, implementing proactive cybersecurity measures for a secure cloud has become important.
However, to better understand cloud security and carve a career in cloud computing, you must begin with Cloud Security Basics, as they are the mainstay of the cloud computing environment.
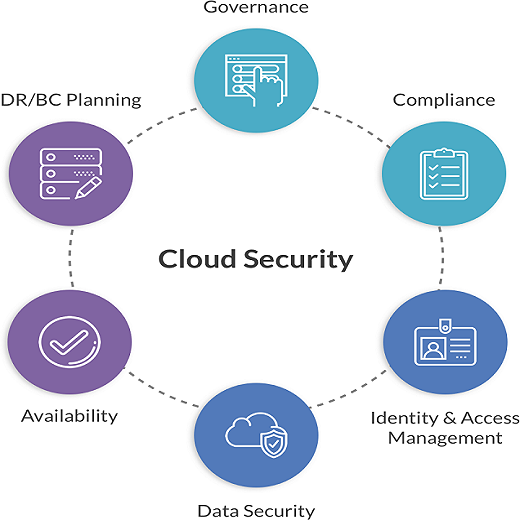
Why Cloud Security is important
The rapid mass adoption of cloud computing and fast-emerging cyber threats drives the need for cloud security. As organizations move more data and workloads to the cloud, companies are concerned about compromising their sensitive data through accidental breaches or sophisticated cyber attacks.
These are the main reasons why cloud data security is important:
Visibility
Organizations access a range of cloud services from multiple devices, departments, and locations. The complexity in the cloud computing environment can obscure visibility within your infrastructure. You cannot see who is using your cloud services and the data or apps they are accessing. This lack of visibility can increase the risk of a data breach or theft.
Compliance
Many compliance regulations require you to have some controls in place and how you store the personally identifiable information (PII) of customers. Non-compliance can put your organization at risk of high penalties, besides losses from cyber attacks.
Business continuity
Network outages and system downtimes can disrupt your operations and affect your bottom line by impacting business continuity.
Factors to consider when implementing cloud security
Unlike traditional, on-premise data storage, the cloud environment is dynamic. In the cloud, the increasing number of users and devices widens the perimeter of the cloud network. It heightens the risk of unauthorized access through account hijacks, breach incidents, and insider threats.
All hardware systems, data, and software require security. You must protect them against increasingly sophisticated cybercrime by keeping pace with the latest security practices that are easily deployable, adaptable, and automated.
Top Ten Cloud Security Best Practices
While operating on the cloud is beneficial, you must also ensure your business systems and IT assets are protected from threats.
Implementing cloud security best practices begin with the identification of security threats to your business. Only if you are aware of the potential risks can you can implement best practices to mitigate the risks.
Here is a list of best practices to help you tackle your cloud security challenges:
1. Select a trusted cloud service provider
Choose a trusted cloud provider that offers the best in-built security protocols and adheres to the industry protocols. A reliable cloud provider holds security certifications and compliances and makes them publicly available.
2. Ensure your cloud services’ visibility
To secure something, you must be able to view it.
Implement a cloud security solution that maintains visibility across the cloud ecosystem. Further, look at granular security plans to cut down security risks.
3. Implement the highest encryption levels
Using the cloud also exposes your IT assets, applications, and data to various threats as they move between your network and the cloud. Implement the highest levels of encryption for your apps, systems, and data, both in transfer and at rest.
Encryption helps you to have complete control over your data and IT assets.
4. Secure your user endpoints
Endpoints are the access points to all cloud processes. Defending the user endpoints to your systems is a key best practice of cloud security. It helps you manage access to the cloud.
Endpoint protection includes securing end-user devices, such as desktops, laptops, and mobile phones. It helps alleviate threats from cybercriminals. Implement an endpoint security solution to protect your devices. Look for solutions that integrate internet security tools, intrusion detection tools, antivirus software, and firewalls.
5. Enforce control of user access
Employees have access to company data and systems. To ensure that they are only able to view or access the resources they need and not beyond, enforcing strict control of user access is a necessary best practice.
Controlling user access through well-entrenched and shared guidelines ensures users have access only to the systems, applications, and data they need for their project. The creation of groups assigns roles and appropriate levels of authorization to grant specific access to company resources. It prevents any unauthorized edits or deletion of information, maintains privacy across multiple projects, and prevents credential theft and insider attacks.
6. Define cloud usage policies
An unambiguous cloud usage policy is a cloud best practice for every organization. Companies must have a strategy for secure use of cloud accounts to ensure that established guidelines are not flouted, and these cloud usage rules must be shared across the organization as a company policy. By monitoring employee usage activities and patterns of access, suspicious cloud activities can be reported, and action can be taken to ensure the 24/7 security of data and applications in the cloud.
7. Implement good password hygiene
Good password hygiene means implementing a robust password to prevent unauthorized access and alteration of data and applications. A password security strategy is part of the company’s cloud security policy. A strong password practice typically requires a minimum of 14 characters with one upper-case letter, one lower-case letter, and one symbol. Additionally, enforcing a password update every 90 days is a healthy password policy to safeguard against malicious attacks.
Deploy multi-factor authentication
Passwords can be hacked into, especially when they are weak. It is estimated that compromised passwords are the cause of 80% of security breaches. Where organizations deal with critical data and applications, or confidential information of customers, the practice of implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security.
MFA requires identity verification of users with secondary evidence and a one-time password/OTP/ biometric verification to access applications and systems.
Go password-less
Companies with MFA may also disengage passwords with password-less authentication apps, enabling businesses to enhance the authentication experience, trim down support costs of password management, and avert risks and costs of data breaches.
8. Monitor activity continuously
With the risks of continuous threats to cloud applications and systems, you must monitor constantly and systematically for any irregular user activity.
Real-time analysis and monitoring can detect abnormal usage patterns, such as user log-in from a new IP address or access from a new device. These are the first warning signals of a potential security breach, so real-time monitoring can trigger alerts and help prevent breach incidents.
A few security best practices include endpoint detection and intrusion detection and response in real-time and vulnerability scanning and remediation.
A few security best practices include endpoint detection and intrusion detection and response in real-time and vulnerability scanning and remediation.
9. Automate onboarding and offboarding
A new employee requires access to applications and systems for their work. But as soon an employee leaves the organization, all access to data and systems must be withdrawn to prevent malicious acts. This is an oft-overlooked aspect by many organizations.
Automation of the onboarding and offboarding process can, however, ensure there are no oversights or delays in de-provisioning user access.
10. Use a Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
Using a CASB is a critical tool to implement cloud security best practices to maximize security controls in the cloud.
It also provides a toolset to execute data security policies, provides complete visibility of the cloud ecosystem, maintains compliance, and enforces threat identification and automated safeguards in real-time.
Bottom line
Executing a rock-solid cloud security strategy is a critical part of cloud migration and use. The aforementioned cloud security best practices help amplify the security of your cloud computing environment. You can not only protect your data, systems, and applications from threats and breaches but also prevent any costs arising from cyber-attacks.